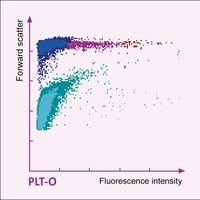
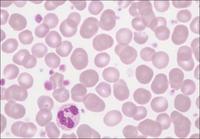
In extreme microcytosis of the erythocytes, for example in severe iron deficiency anaemia, the microcytes may be falsely classified as platelets when assessed by impedance counting, simulating thrombocytosis. However, in such a case fluorescent staining and counting of platelets in the optical channel will always provide a correct result. The scattergram shows a real thrombocytosis (1,023,000/µL).

|
|
|
|